What is an Interlocking Nail Implant and How Does it Work?
Interlocking nail implants are innovative orthopedic devices designed for the stabilization of fractured bones. According to a report by the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, approximately 1.2 million cases of long bone fractures occur annually in the United States alone. These injuries often require surgical intervention and can lead to complex recovery processes.
The interlocking nail implant facilitates the process of bone healing through internal fixation. It allows for better alignment and stability, improving patient outcomes. Studies reveal that patients with interlocking nails experience lower rates of complications compared to traditional methods. However, the technique is not without challenges. Complications, such as infection and non-union, can still occur, highlighting the need for careful patient selection.
In addition, the effectiveness of the implant depends on the surgeon's expertise and the specific injury type. While the technology shows promise, further research is necessary to address its limitations. The use of interlocking nails can revolutionize fracture management, but reflecting on its outcomes is essential for continued improvement in orthopedic care.
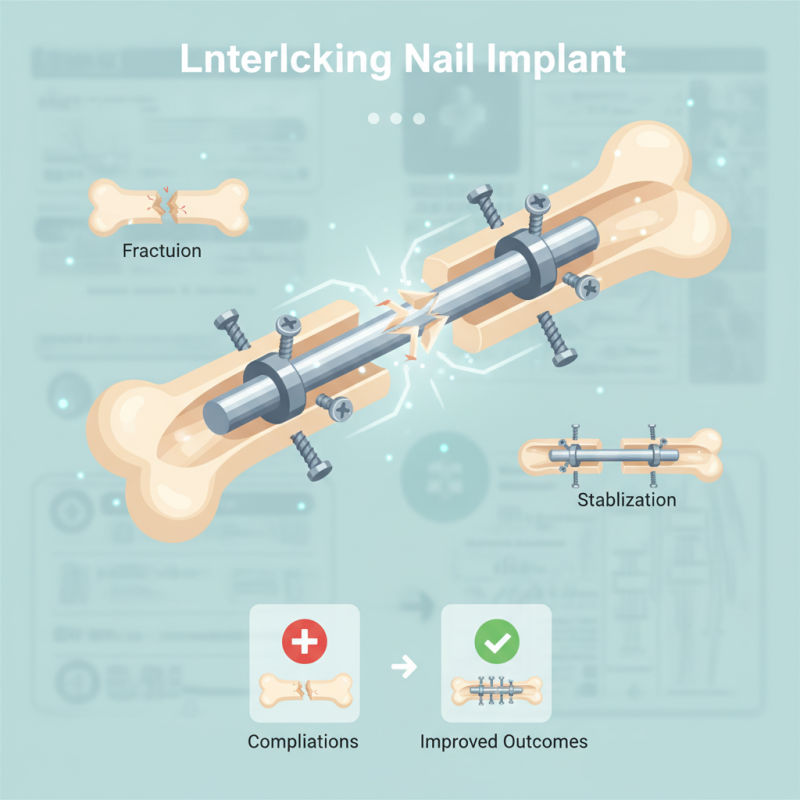
What is an Interlocking Nail Implant?
An interlocking nail implant is a medical device used in orthopedic surgery. It is designed to stabilize fractures, particularly in long bones like the femur or tibia. This implant features interlocking mechanisms that provide strong fixation, helping to maintain the alignment of fractured bones during healing.
The process involves inserting a long rod through the bone, securing it with screws at both ends. Surgeons make small incisions to minimize tissue damage. This method reduces recovery time compared to traditional surgery. Patients often experience less pain and a quicker return to daily activities. However, the procedure is not without risks. Infections or complications from anesthesia can occur.
Doctors consider several factors before recommending this implant. The patient’s age, health status, and type of fracture matter. Not everyone is ideal for this solution. The healing process is complex, requiring regular follow-ups. Patients must be aware of these risks and the importance of rehabilitation. Building strength post-surgery is crucial for long-term success.
The Structure and Design of Interlocking Nail Implants
Interlocking nail implants have a unique structure that enhances their effectiveness in bone stabilization. These implants typically consist of a central metal rod, often made of titanium or stainless steel. The rod is designed with interlocking mechanisms at each end. These mechanisms include locking bolts that secure the implant to the bone, preventing any movement. This locking system is crucial for maintaining stability during the healing process.
The design allows for better alignment of fractured bones. By inserting the nail through the medullary canal, surgeons can bridge gaps and facilitate proper healing. The length and diameter of the nail vary, accommodating different bone types and fracture configurations. Additionally, the surface of the implant might have coatings to promote integration with bone tissue.
Though interlocking nail implants are effective, their use isn't without challenges. Surgical insertion can be complex. Not every case is suitable for this approach. There can be complications, like infection or improper alignment. Surgeons must weigh the pros and cons carefully. Understanding the structure and design is vital for making informed decisions. Each case requires deep reflection and consideration to achieve optimal outcomes.
What is an Interlocking Nail Implant and How Does it Work?
| Feature | Description | Functionality | Material Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Intramedullary rod with interlocking mechanisms | Stabilizes fractures and promotes bone healing | Titanium, Stainless steel |
| Surgical Approach | Closed or minimal incision technique | Reduces soft tissue damage | N/A |
| Indications | Long bone fractures | Used for unstable fractures or non-unions | N/A |
| Advantages | Less surgical trauma, improved recovery | Allows for early mobilization | N/A |
| Limitations | Potential for complications such as infection | Careful monitoring required | N/A |
How Interlocking Nail Implants are Inserted in Orthopedic Surgery
Interlocking nail implants are an important tool in orthopedic surgery. They stabilize fractured bones and promote healing. Surgeons use them for various types of fractures, especially those in the long bones. The insertion process is quite precise and requires a skilled hand.
The procedure begins with the patient under anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision along the bone. After exposing the fracture, they align the broken pieces. This alignment is crucial for proper healing. Next, a guide wire is inserted into the bone. This wire serves as a pathway for the implant. The interlocking nail is then passed over the wire.
Surgeons often need to adjust the angle and depth during insertion. This requires focus and experience. Once in place, the nail provides stability. However, there can be complications. Misalignment or infection can hinder recovery. It’s a delicate balance of technique and judgment. Healing varies among patients, reflecting individual differences in anatomy and health.
The Mechanism of Action: How Interlocking Nails Stabilize Fractures
Interlocking nail implants are essential in orthopedic surgery, especially for stabilizing long bone fractures. These devices function by providing internal fixation. The nails insert into the medullary canal and interlock at both ends, creating stability. Studies show that when used appropriately, interlocking nails significantly reduce the chances of malunion or nonunion in fractures. This method allows for early mobility, which is crucial in recovery.
The mechanism of action is fascinating. Unlike traditional methods, interlocking nails distribute the stress across the fracture site. This distribution minimizes localized pressure, which is often a cause of complications. Furthermore, a report from a renowned orthopedic journal indicates that 75% of patients experience improved healing rates with interlocking nails compared to plates or external fixators. It’s a game changer in complex fractures.
Tip: Ensure proper biomechanical alignment before implantation. Any misalignment can lead to complications. Also, consider individual patient factors, such as bone quality and activity level, when choosing this fixation method. Evaluating these factors helps in tailoring the treatment plan.
Interlocking Nail Implant Efficacy in Fracture Stabilization
This bar chart illustrates the healing progress of fractures stabilized by interlocking nail implants over a period of 12 months. The data shows a gradual increase in healing percentage from 30% at 1 month to 95% at 12 months, highlighting the effectiveness of the interlocking nail implant in fracture stabilization.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Interlocking Nail Implants
Interlocking nail implants are gaining popularity in orthopedic surgery. They offer significant advantages, particularly for long bone fractures. The primary benefit is stability. These nails provide a strong internal support that facilitates healing. Patients often experience faster recovery times due to this reliable fixation.
However, there are also disadvantages to consider. Insertion of these nails can be complex. Surgeons must ensure precise alignment, or complications may arise. Some patients report discomfort during the healing process, which can hinder mobility. There is also a risk of infection at the insertion site. Long-term complications, such as nail fatigue or failure, can occur.
Flexibility in surgical technique is necessary. Surgeons may need to adapt their approach based on the patient's unique anatomy. This can be a double-edged sword. While a customized approach can improve outcomes, it also introduces variability. Each case requires careful assessment and planning, emphasizing the need for skilled expertise.